As IoT devices become smarter and more widespread, businesses face a crucial decision: Should your devices process data at the edge, or send it to the cloud?
Both edge computing and cloud computing play vital roles in IoT infrastructure, but understanding the difference and which is right for your setup can dramatically improve performance, efficiency, and scalability.
What Is Cloud Computing for IoT?
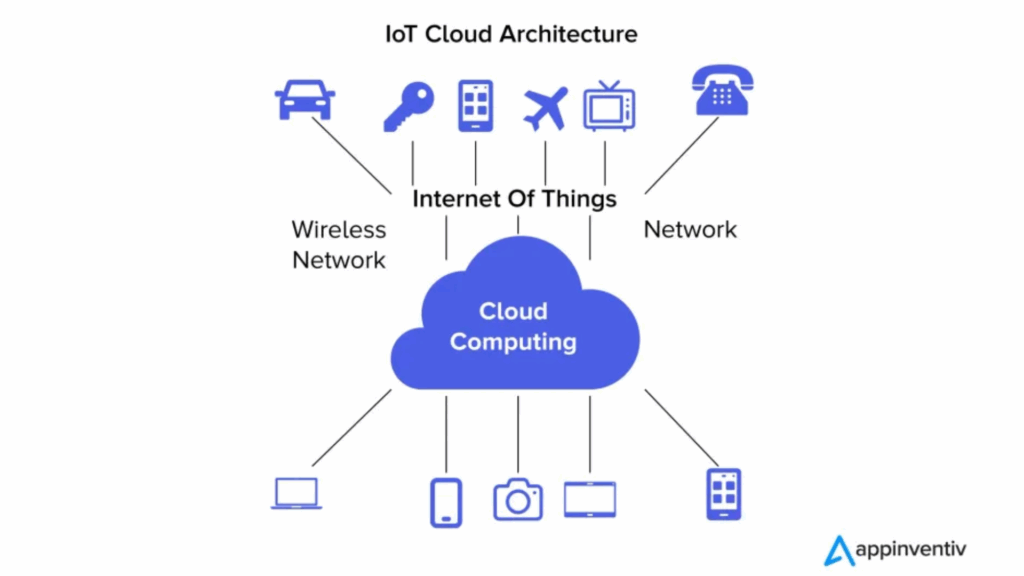
Cloud computing involves sending data from IoT devices to centralized data centers for storage, processing, and analysis. This is ideal for applications that don’t need real-time responsiveness, such as:
- Long-term analytics
- Data backups
- Large-scale processing
- Historical trend monitoring
Pros of Cloud Computing:
- Scalable storage and computing power
- Centralized data management
- Easier updates and deployments
Cons:
- Latency issues
- Dependency on internet connection
- Privacy concerns with data transfer
What Is Edge Computing for IoT?
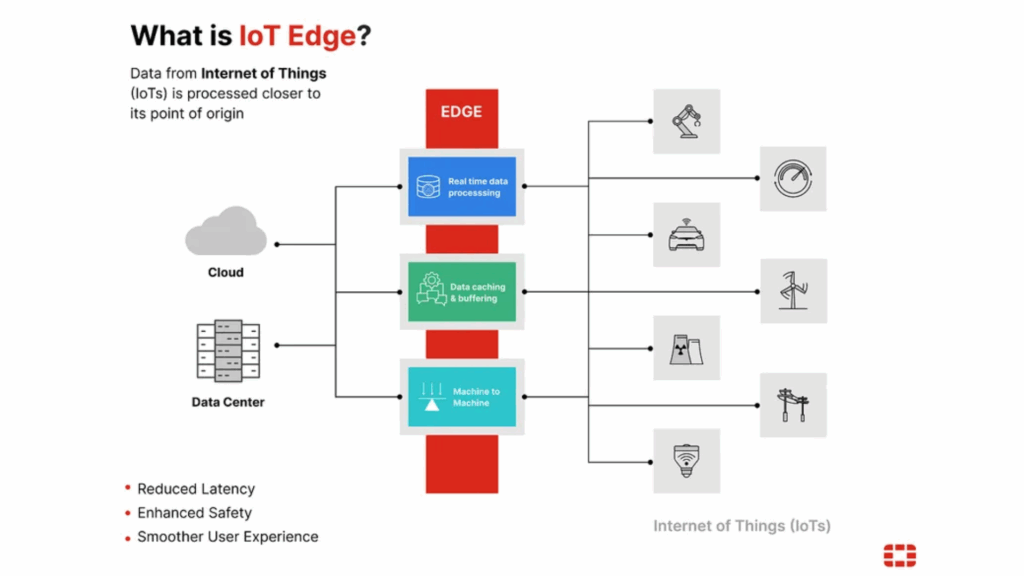
Edge computing means processing data locally on the device or a nearby edge node instead of relying entirely on the cloud. This is perfect for applications where speed and autonomy are essential, like:
- Industrial automation
- Healthcare monitoring
- Smart vehicles
- Security systems
Pros of Edge Computing:
- Real-time data processing
- Reduced bandwidth usage
- Enhanced data privacy
- Lower latency
Cons:
- Limited processing power
- More complex device management
- Scalability challenges
So, Which One Is Better?
There’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Choosing between edge and cloud depends on:
- Latency sensitivity: Choose edge if milliseconds matter.
- Connectivity: Use edge in remote or offline environments.
- Data volume: Use cloud for high-capacity analysis and storage.
- Security needs: Edge can keep sensitive data local.
- Budget: Cloud services can get expensive with frequent transfers.
Explore more to dive deeper into the differences between edge and cloud.
Pro Tip: A hybrid approach often delivers the best results — edge computing for real-time responses, and cloud computing for data aggregation and learning.
How VLO Labs Helps You Decide
VLO Labs specializes in helping businesses design and deploy custom AI and IoT solutions that balance edge and cloud computing effectively.
Whether you’re creating a smart wearable, industrial device, or logistics tracker, VLO Labs ensures your product is engineered for efficiency, scalability, and performance. They help clients:
- Build edge-ready IoT hardware
- Optimize AI models for real-world deployment
- Design secure cloud-to-device communication pipelines
- Navigate regulatory and connectivity challenges
Their full-stack approach allows startups and enterprises alike to get to market faster with reliable, scalable tech. Click here to learn why startups trust VLO Labs for smart solutions!
Best Use Cases: Edge vs. Cloud in Action
| Application Type | Best Fit |
|---|---|
| Smart Home Devices | Edge + Cloud |
| Industrial Robotics | Edge |
| Smart Agriculture | Edge |
| Logistics & Tracking | Cloud |
| Predictive Analytics | Cloud |
| Medical Monitoring | Edge |
Final Thoughts
Ultimately, when it comes to IoT, edge and cloud aren’t competitors — they’re partners. The right balance between the two can save costs, improve efficiency, and deliver a better experience for users.
Therefore, with experienced partners like VLO Labs, you can make sure your IoT ecosystem is built for both today’s demands and tomorrow’s growth.